Introduction
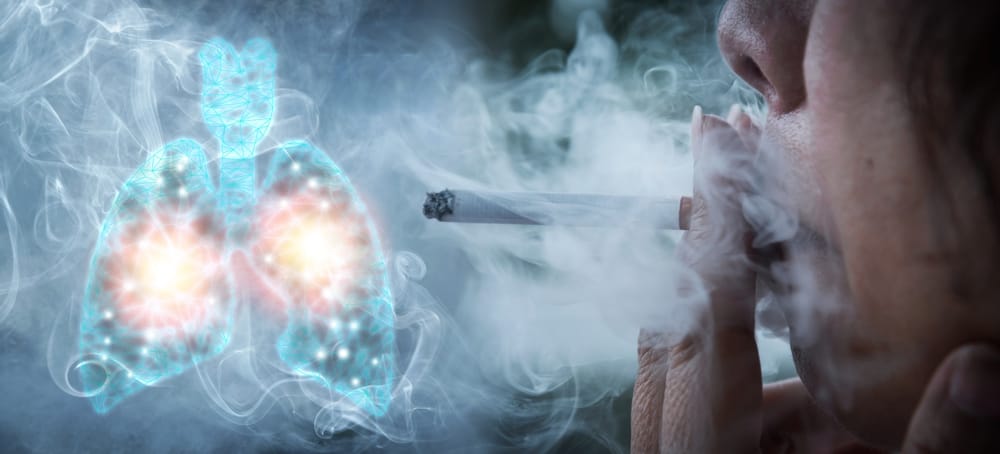
Smoking, the single most preventable cause of premature death worldwide, claims over 7 million lives annually. Lung diseases are among the most devastating consequences of smoking, affecting millions globally. In this blog, we’ll delve into the alarming connection between smoking and lung diseases, exploring the risks, consequences, and paths to quitting.
The Risks: Smoking’s Impact on Lungs
Smoking damages lung tissue, inflames airways, and destroys lung function. This leads to:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Progressive lung damage, causing breathing difficulties.
- Lung Cancer: Smoking accounts for 80% of lung cancer deaths.
- Emphysema: Irreversible lung damage, reducing oxygen exchange.
- Chronic Bronchitis: Inflammation and congestion in airways.
- Pneumonia: Increased risk of pneumonia, especially among smokers with underlying lung conditions.
Consequences: The Toll of Smoking
- Reduced lung function and breathing capacity
- Increased risk of respiratory infections
- Decreased quality of life
- Financial burden: smoking-related healthcare costs are extremely high
- Premature death: smoking reduces life expectancy by 10-15 years
Quitting Smoking: Paths to Recovery
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): Gum, patches, lozenges, or inhalers.
- Prescription Medications: Bupropion or varenicline.
- Counseling: Individual or group support.
- Support Groups: Online forums or local meetups.
- Alternative Methods: Acupuncture, hypnosis, or meditation.
Breaking Free from Smoking
Quitting smoking requires determination and support. Take the first step:
- Set a quit date.
- Consult a healthcare provider.
- Explore NRT and prescription options.
- Join a support group.
- Stay committed.
Conclusion
Smoking’s link to lung diseases is undeniable. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to prevent lung damage and protect your health. Take control, break free, and breathe easier.
Disclaimer: Consult a pulmonologist before starting any quit-smoking program.